
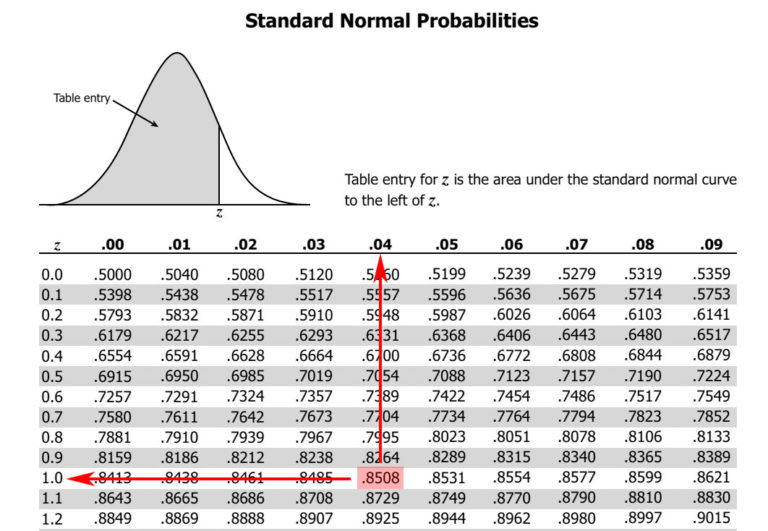
Probability of getting a value greater than 2.74 = 1-0.9690 = 0.0031. We can calculate the p-value as follows: We will look for the value of F(Z) where Z = 2.74. Regardless of Ha, z (p - p0) / sqrt (p0 (1. The distribution for z is the standard normal distribution it has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. To calculate the p-value from z score, choose the normal distribution and enter the z score in the statistic field. If the test statistic is -2.74 or 2.74, we will reject the null hypothesis. Realize P (z -1.83) P (z 1.83) since a normal curve is symmetric about the mean. Reject the null hypothesis if test-statistic =2.17Ģ.17 is the value of z in z-table where F (Z) is (1 – 0.015) = 0.985 In a two-tailed hypothesis test, the decision rule will be as follows:Īssume that the level of significance is 3% (a = 0.03) Since p-value (0.011) is less than a (0.04), we reject the null hypothesis. Under p-value approach, the decision rule will be as follows: We can calculate the p-value as follows: We will look for the value of F(Z) where Z=2.29. If the test statistic is 2.29, we will reject the null hypothesis. Z-score to percentile calculator (p-value from Z score) for both one-sided and two-sided p-values. The Z-score is found by assuming that the null hypothesis is true, subtracting the assumed. Use this Z to P calculator to easily convert Z-scores to P-values (one or two-tailed) and see if a result is statistically significant.
#Z score to p value how to#
Reject the null hypothesis if test-statistic 1.75ġ.75 is the value of z in z-table where F (Z) is (1 – 0.04) = 0.96 A z-score equal to 1 represents an element, which is 1 standard deviation greater than the mean a z-score equal to 2 signifies 2 standard deviations greater. We first look at how to calculate the p value using the Z-score. Under critical value approach, the decision rule will be as follows: In a left-tailed hypothesis test, the decision rule will be as follows:Īssume that the level of significance is 10% (a = 0.10) This will depend on whether it’s a two-tailed or a one-tailed test. Tests of the true value of an unknown population mean can be either one-tailed (left. Once we have the test statistic, we look into the z-table to calculate a value greater than or less than that. Z Tests and P-Values: Testing Hypotheses: is known and n > 30. The p-value is the probability, computed using the test statistic, that measures the support (or lack of support) provided by the sample for the null hypothesis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
